[ad_1]
But according to leaked U.S. intelligence documents produced in February and March, the supply of air defense systems and their munitions pose a significant and growing problem, as Ukraine uses up their limited stocks to keep up with constant bombardments. Kyiv risks running low on their most common Soviet-era systems, the documents warned, forcing commanders to select what can and cannot be shot down.
That dynamic underscores the inherent challenge, experts have said: Air defense is a difficult mission using expensive and finite resources, with no silver bullets. To address that, the West has ramped up its commitments to Ukraine, sending a range of gear, from truck-mounted guns to the most modern missile-killing systems the United States has to offer.
Here is a rundown of the Western-provided systems Ukraine now has, and what they can do.
The Patriot is the U.S. military’s most advanced air defense system, with a range of roughly 20 to 100 miles, depending on the threat. It was designed as an antiaircraft system, but newer variants of Patriot can also engage ballistic and cruise missiles and drones.
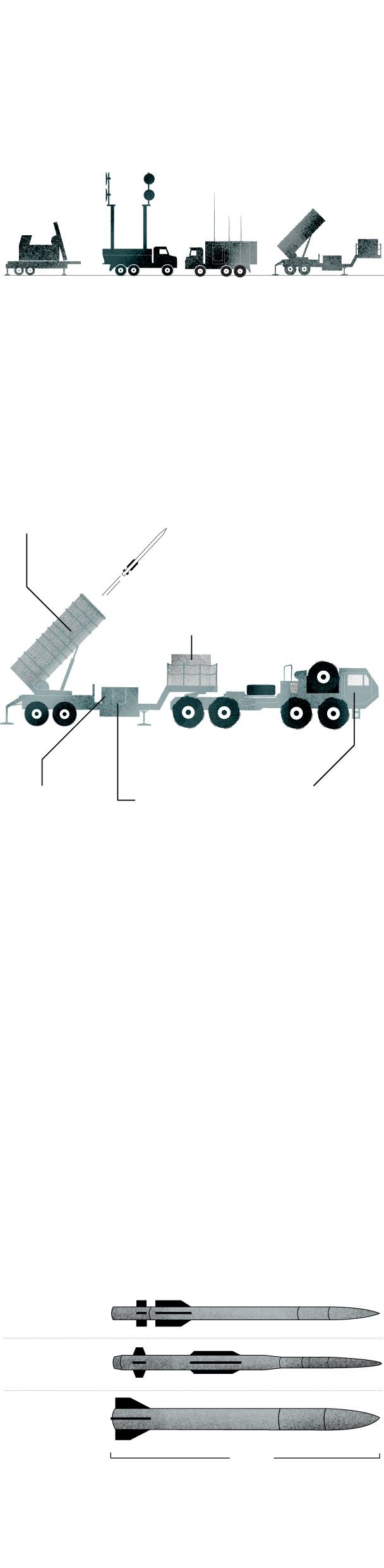
A typical Patriot battery includes a radar set, engagement control station, power generation and several launch stations.
Missile Canisters
These canisters store the Patriot’s interceptors. Each one can carry four PAC-3 missiles, for a total of 16 rounds on each launcher.
Power generator
It provides the power to run the launching station’s electrical systems.
Launcher Electronics Module
It houses the launcher’s power as well as the launch and motor control units.
Datalink
Terminal
Module
It maintains a radio digital data link between the station and a remote engagement control station.
Tow Truck
It can remain attached to the launcher during launch operations or it can detach.
Some newer models of these systems have different capabilities and equipment than previous iterations.
PAC-2 and PAC-3, two families
of interceptors
The missile is command-guided near the target. In its terminal phase, it uses Track-Via-Missile (TVM) guidance to track the target as it is illuminated by the ground-based engagement radar.
Source: Center for Strategic and International Studies
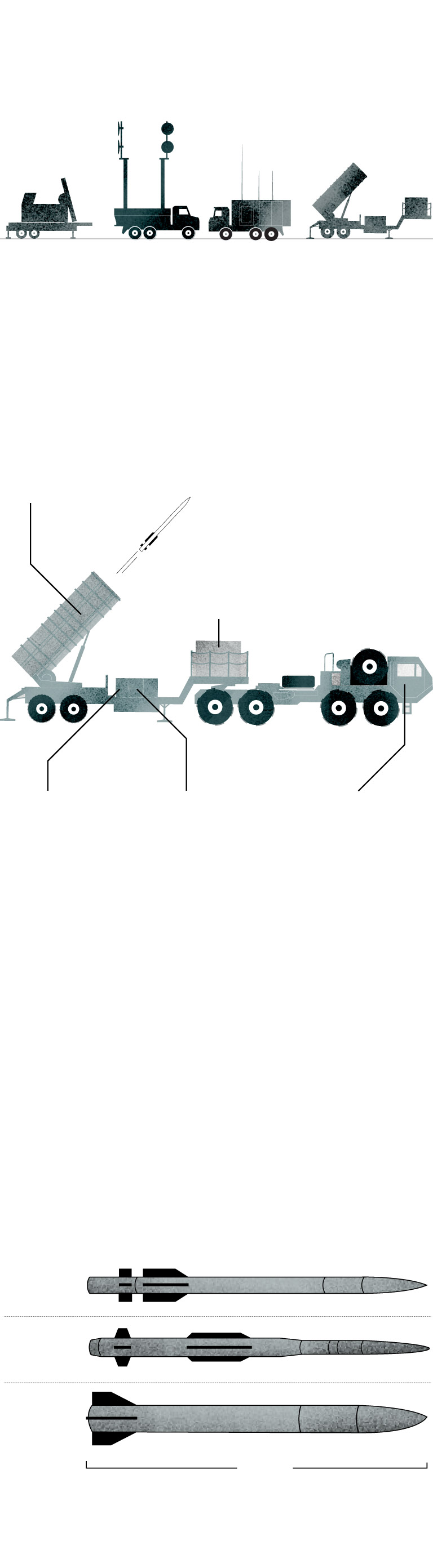
A typical Patriot battery includes a radar set, engagement control station, power generation and several launch stations.
Missile Canisters
These canisters store the Patriot’s interceptors. Each one can carry four PAC-3 missiles, for a total of 16 rounds on each launcher.
Power generator
It provides the power to run the launching station’s electrical systems.
Datalink
Terminal
Module
It maintains a radio digital data link between the station and a remote engagement control station.
Launcher Electronics Module
It houses the launcher’s power as well as the launch and motor control units.
Tow Truck
It can remain attached to the launcher during launch operations or it can detach.
Some newer models of these systems have different capabilities and equipment than previous iterations.
PAC-2 and PAC-3, two families
of interceptors
The missile is command-guided near the target. In its terminal phase, it uses Track-Via-Missile (TVM) guidance to track the target as it is illuminated by the ground-based engagement radar.
Source: Center for Strategic and International Studies
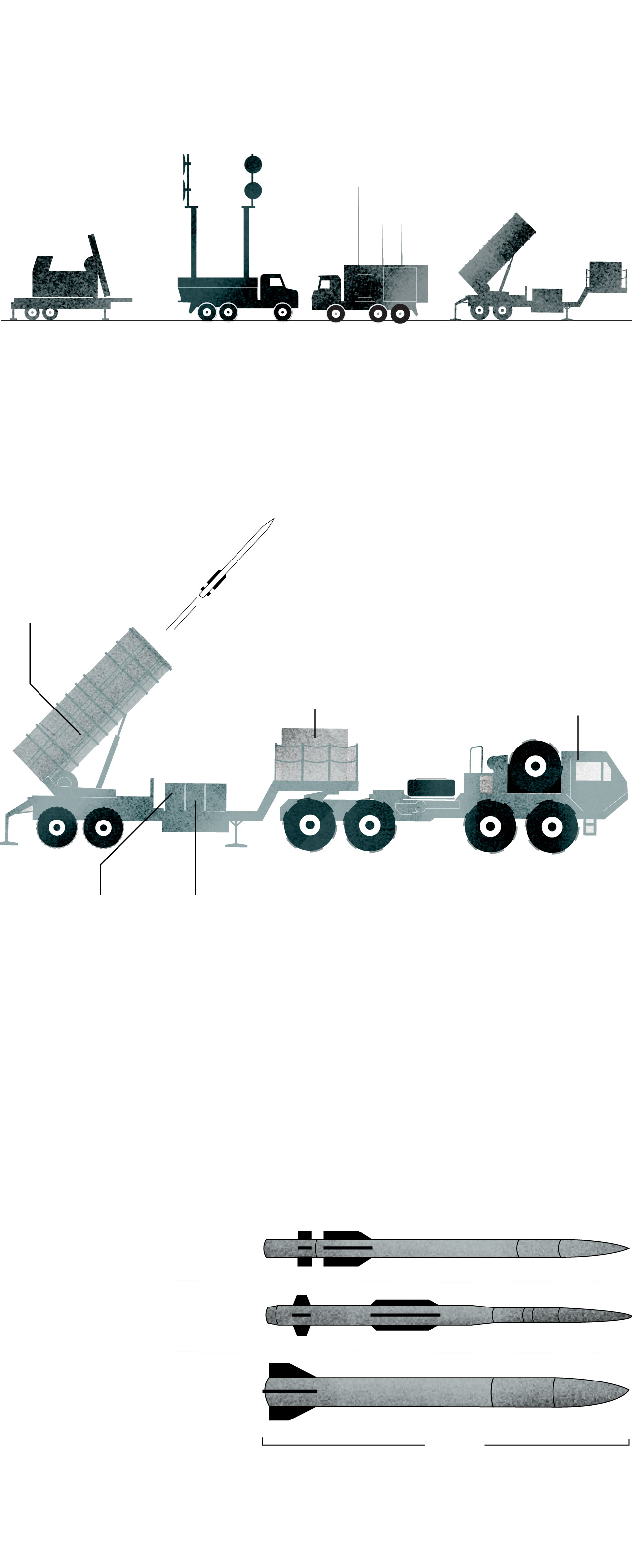
A typical Patriot battery includes a radar set, engagement control station, power generation and several launch stations.
Missile Canisters
These canisters store the Patriot’s interceptors. Each one can carry four PAC-3 missiles, for a total of 16 rounds on each launcher.
Tow Truck
It can remain attached to the launcher during launch operations or it can detach.
Power generator
It provides the power to run the launching station’s electrical systems.
Launcher Electronics Module
It houses the launcher’s power as well as the launch and motor control units.
Datalink Terminal Module
It maintains a radio digital data link between the station and a remote engagement control station.
Some newer models of these systems have different capabilities and equipment than previous iterations.
PAC-2 and PAC-3, two families of interceptors
The missile is command-guided near the target. In its terminal phase, it uses Track-Via-Missile (TVM) guidance to track the target as it is illuminated by the ground-based engagement radar.
Source: Center for Strategic and International Studies
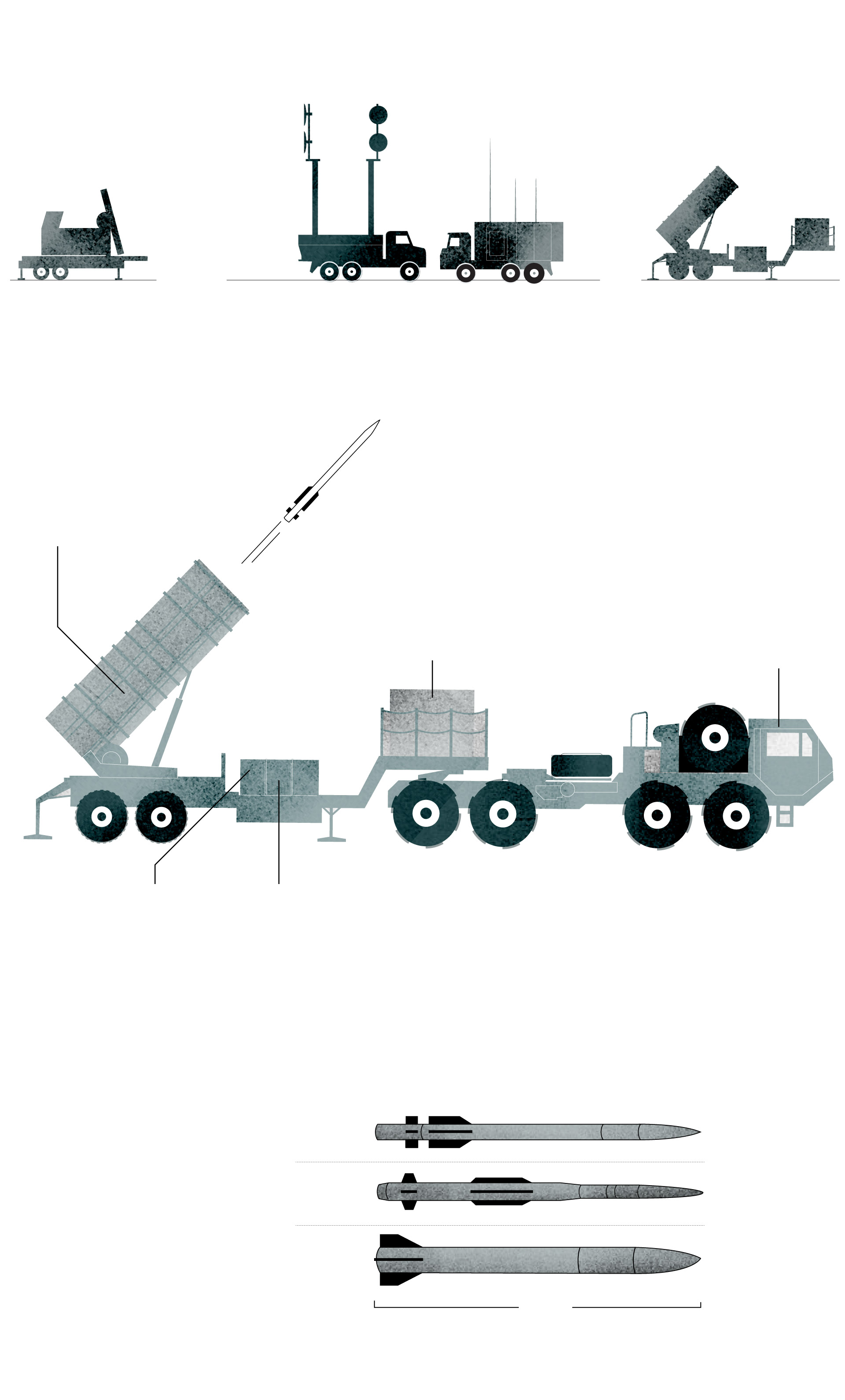
A typical Patriot battery includes a radar set, engagement control station, power generation and several launch stations.
Missile Canisters
These canisters store the Patriot’s interceptors. Each one can carry four PAC-3 missiles, for a total of 16 rounds on each launcher.
Power generator
It provides the power to run the launching station’s electrical systems.
Tow Truck
It can remain attached to the launcher during launch operations or it can detach.
Datalink Terminal Module
It maintains a radio digital data link between the station and a remote engagement control station.
Launcher Electronics Module
It houses the launcher’s power as well as the launch and motor control units.
Some newer models of these systems have different capabilities and equipment than previous iterations.
PAC-2 and PAC-3, two families of interceptors
The missile is command-guided near the target. In its terminal phase, it uses Track-Via-Missile (TVM) guidance to track the target as it is illuminated by the ground-based engagement radar.
Source: Center for Strategic and International Studies
Along with missiles, a Patriot battery includes radars and control stations to identify, track and target enemy weapons.
The locations of Ukraine’s two Patriot systems are a closely kept secret, though one recently used to take down missiles is based in or around Kyiv, according to a U.S. defense official.
Reliance on the Patriot will test the ability of the United States and the West to balance their needs to safeguard their own stocks while providing assistance to Ukraine. Each Patriot interceptor missile costs an estimated $4 million, putting a premium on each decision to fire. Ukrainian officials have said one Russian strategy is to attempt to exhaust air defense systems by saturating the sky with targets, some of which are decoys meant to confuse the interceptor, allowing the real missile to slip through.
The NASAMS suite — short for National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile Systems — includes a command post, sensors, a radar system and munitions that can be fired from a stand-alone pod or from the back of a truck. This is the air defense system used to protect the White House.
Its radar can detect threats up to roughly 80 miles away, depending on variables including the weather and the size and altitude of a target.
The NASAMS utilizes the same kind of missiles already in common use with Western fighter jets, so their weapon stocks are cheaper and more widely available than the costly Patriot interceptors.
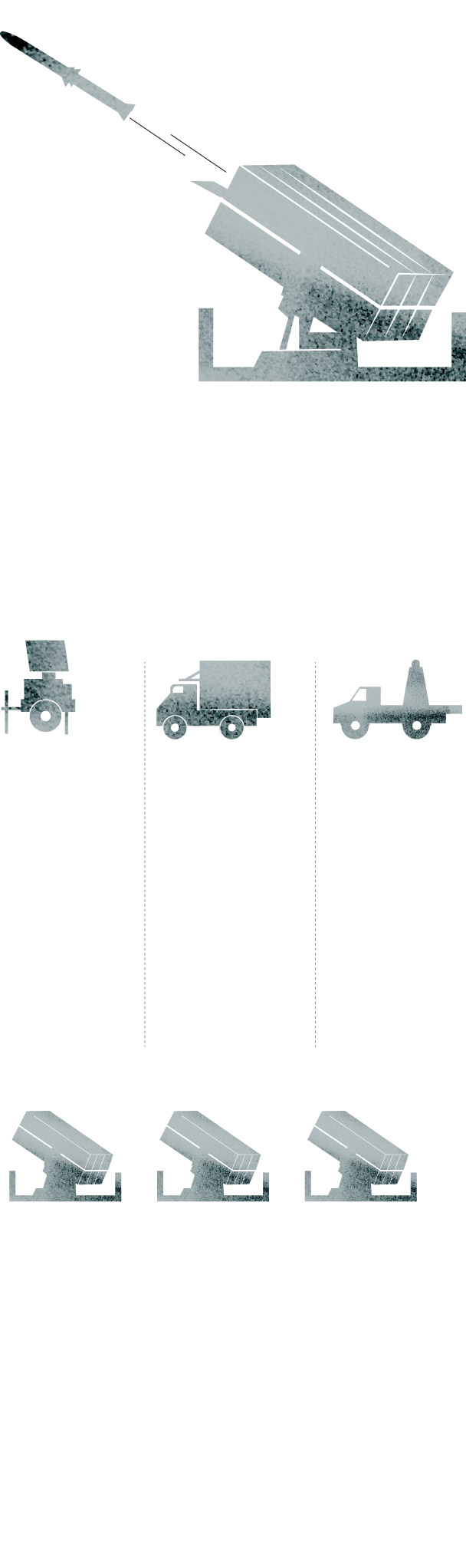
NASAMS (National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System) is a short-to-medium-range ground-based air defense system. It was designed and manufactured by the Norwegian company Kongsberg, which teamed up with the American company Raytheon for the missile.
Fire
Distribution Center
Provides battle management
command, control,
communications,
computers
and intelligence.
Electro-Optical (EO) sensor
Provides data to the Fire Distribution
Center to
monitor threats.
MPQ-64 F1 Radar
It detects,
tracks, identifies,
classifies and
reports airborne
threats.
The NASAMS is equipped with three multi-missile launchers, each carrying up to six missiles inside the protective canisters.
The launcher transports, aims and fires missiles with different characteristics.
Sources: Kongsberg, Raytheon, Army Recognition Group.
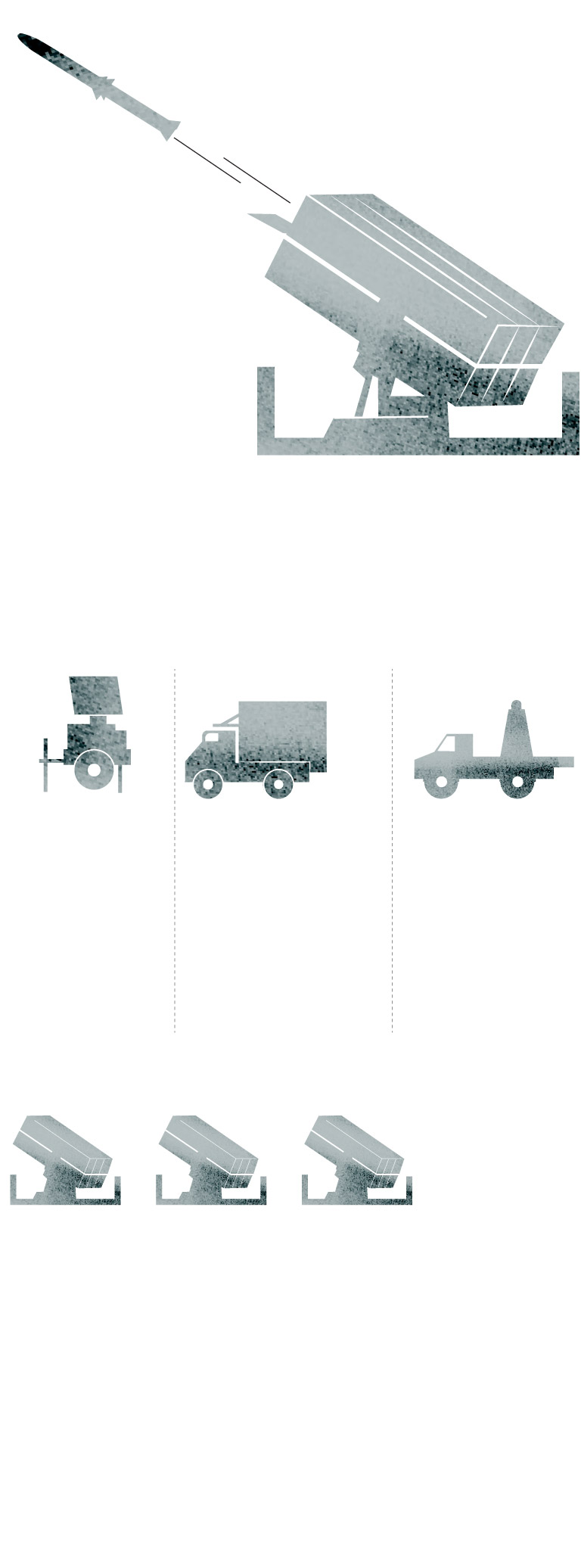
NASAMS (National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System) is a short-to-medium-range ground-based air defense system. It was designed and manufactured by the Norwegian company Kongsberg, which teamed up with the American company Raytheon for the missile.
MPQ-64 F1
Radar
It detects,
tracks, identifies,
classifies and
reports airborne
threats.
Fire Distribution
Center
Provides battle
management
command, control,
communications,
computers
and intelligence.
Electro-Optical
(EO) sensor
Provides data to
the Fire Distribution
Center to
monitor threats.
The NASAMS is equipped with three multi-missile launchers, each carrying up to six missiles inside the protective canisters.
The launcher transports, aims and fires missiles with different characteristics.
Sources: Kongsberg, Raytheon, Army Recognition Group.
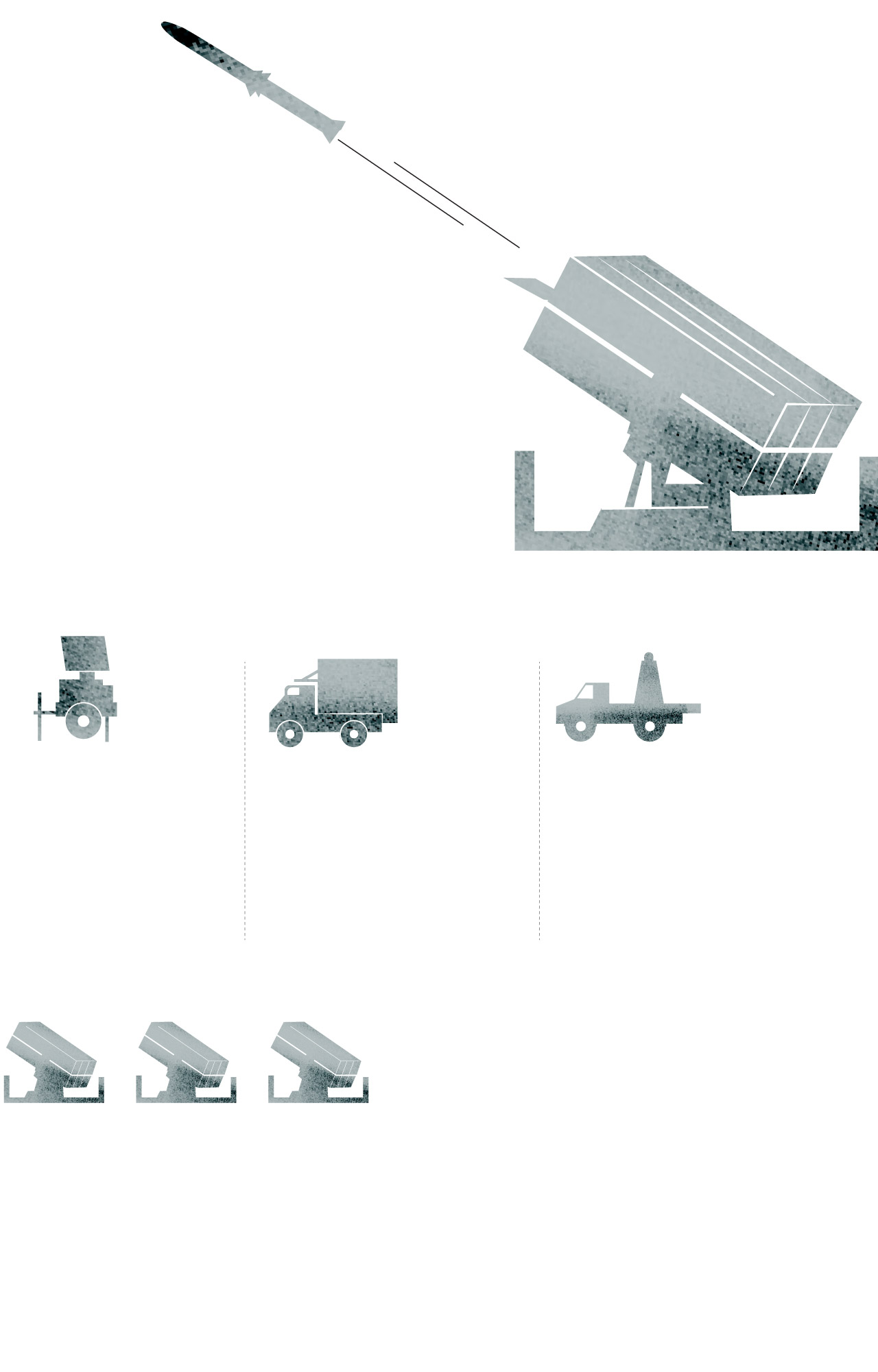
NASAMS (National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System) is a short-to-medium-range ground-based air defense system. It was designed and manufactured by the Norwegian company Kongsberg, which teamed up with the American company Raytheon for the missile.
MPQ-64 F1 Radar
It detects,
tracks, identifies,
classifies and
reports airborne
threats.
Fire Distribution Center
Provides battle
management command,
control, communications,
computers and intelligence.
Electro-Optical (EO) sensor
Provides data to the Fire
Distribution Center to
monitor threats.
The NASAMS is equipped with three multi-missile launchers, each carrying up to six missiles inside the protective canisters.
The launcher transports, aims and fires missiles with different characteristics.
Sources: Kongsberg, Raytheon, Army Recognition Group.
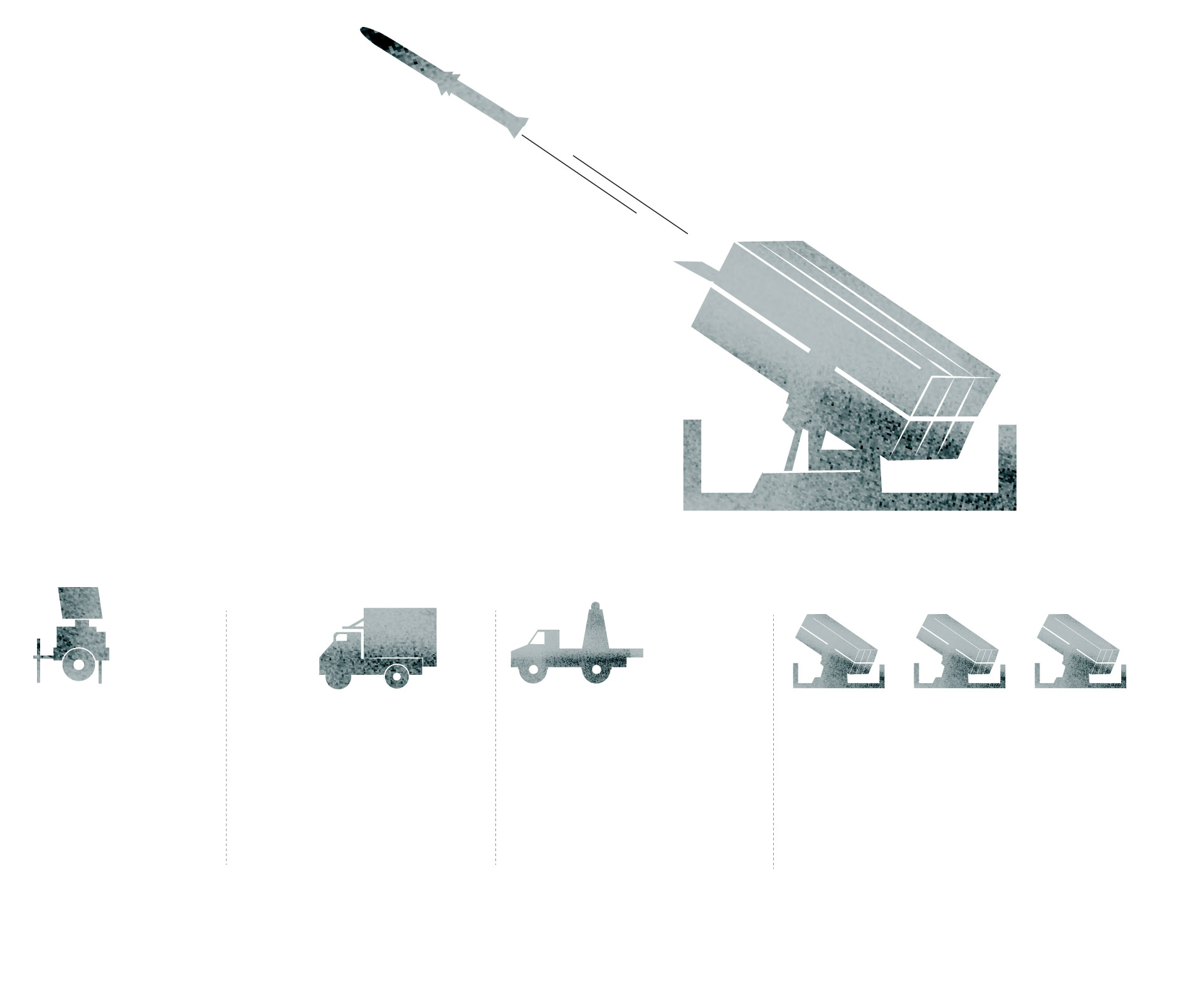
NASAMS (National Advanced Surface to Air Missile System) is a short-to-medium-range ground-based air defense system. It was designed and manufactured by the Norwegian company Kongsberg, which teamed up with the American company Raytheon for the missile.
MPQ-64 F1 Radar
It detects,
tracks, identifies,
classifies and
reports airborne
threats.
Fire Distribution Center
Provides battle
management command,
control, communications,
computers and intelligence.
Electro-Optical (EO) sensor
Provides data to the Fire
Distribution Center to
monitor threats.
Launchers
The NASAMS is equipped with three
multi-missile launchers, each carrying
up to six missiles inside the protective canisters.
The launcher transports, aims and fires missiles
with different characteristics.
Sources: Kongsberg, Raytheon, Army Recognition Group.
The German IRIS-T system is similar to NASAMS. It’s a tier below the Patriot system and is configured to use missiles initially designed for fighter jets.
The heat-seeking missile has a medium range of around 20 miles and has proved effective against Russian cruise missiles, said Ian Williams, deputy director of the Missile Defense Project at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. “The problem with [the IRIS-T] is sourcing it,” Williams added. Germany has pledged more, but they’re still in production, he said.
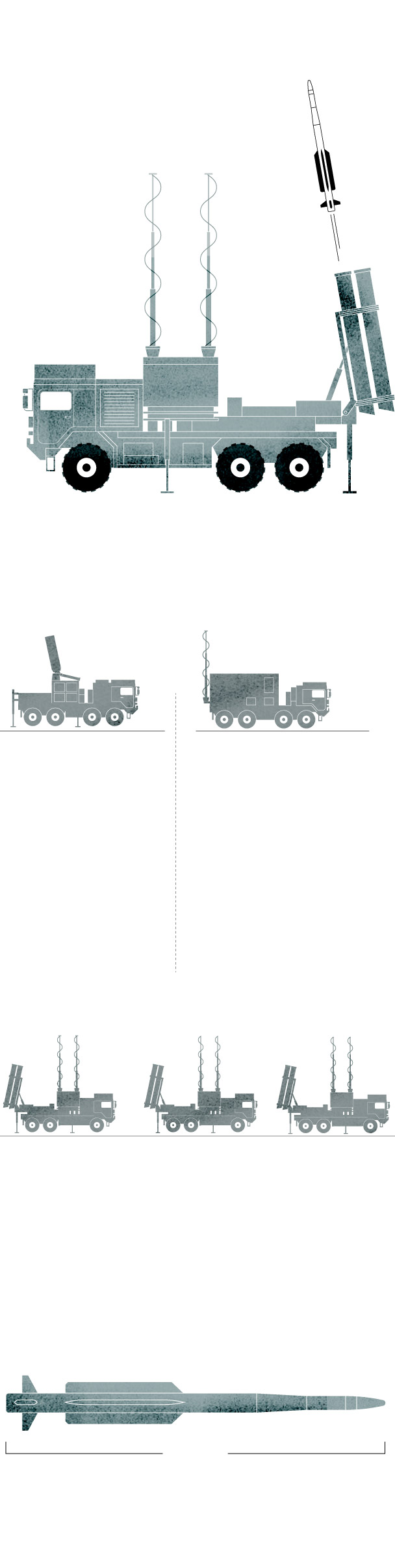
IRIS-T SL system
components
The IRIS-T SL
is a mobile air defense missile system designed and developed by the German company Diehl.
Command and Control System
It performs fire control used to conduct airspace surveillance and has the capability to evaluate aerial treats and weapon assignments.
Radar
The system includes a multifunction radar with a range of 250 km (155 miles).
Launcher
The launcher vehicle can be based on a truck chassis or a tracked armored chassis. In the firing position, the container missile launchers are erected in the vertical position.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
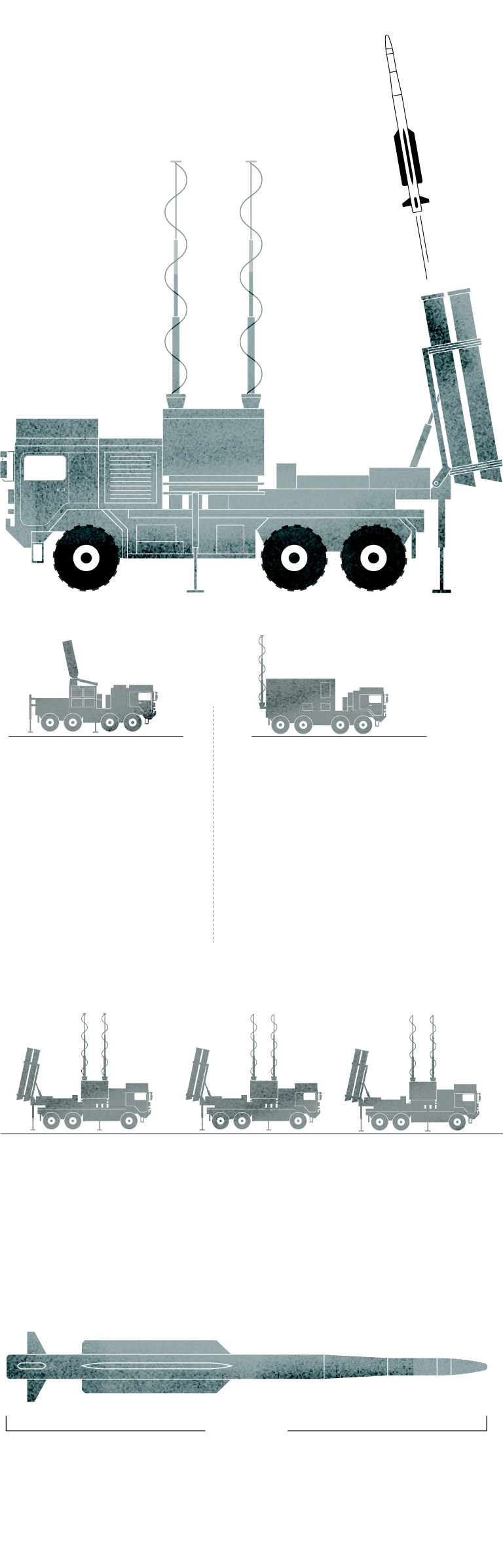
IRIS-T SL system
components
The IRIS-T SL is a mobile air defense missile system designed and developed by the German company Diehl.
Radar
The system includes a multifunction radar with a range of 250 km (155 miles).
Command and Control System
It performs fire control used to conduct airspace surveillance and has the capability to evaluate aerial treats and weapon assignments.
Launcher
The launcher vehicle can be based on a truck chassis or a tracked armored chassis. In the firing position, the container missile launchers are erected in the vertical position.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
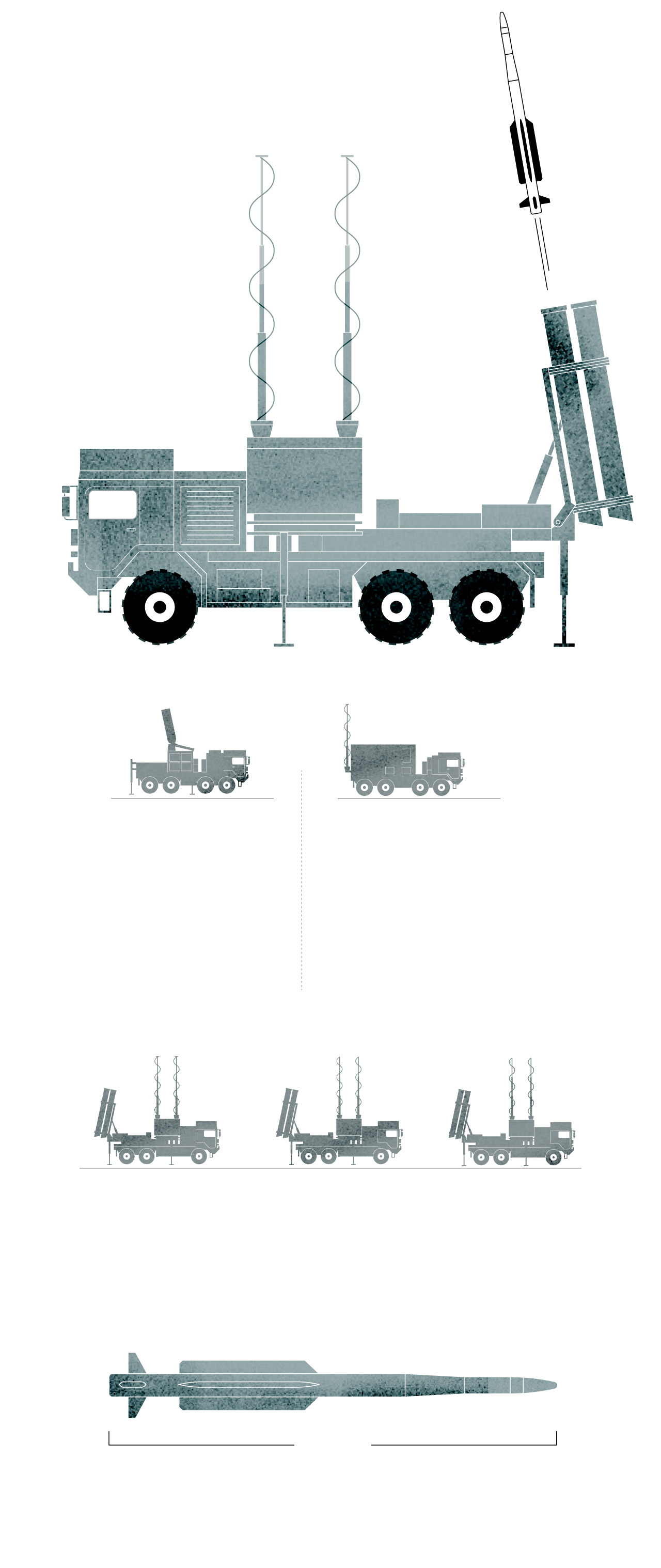
IRIS-T SL system
components
The IRIS-T SL is a mobile air defense missile system designed and developed by the German company Diehl.
Radar
The system includes a multifunction radar with a range of 250 km (155 miles).
Command and Control System
It performs fire control used to conduct airspace surveillance and has the capability to evaluate aerial treats and weapon assignments.
Launcher
The launcher vehicle can be based on a truck chassis or a tracked armored chassis. In the firing position, the container missile launchers are erected in the vertical position.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
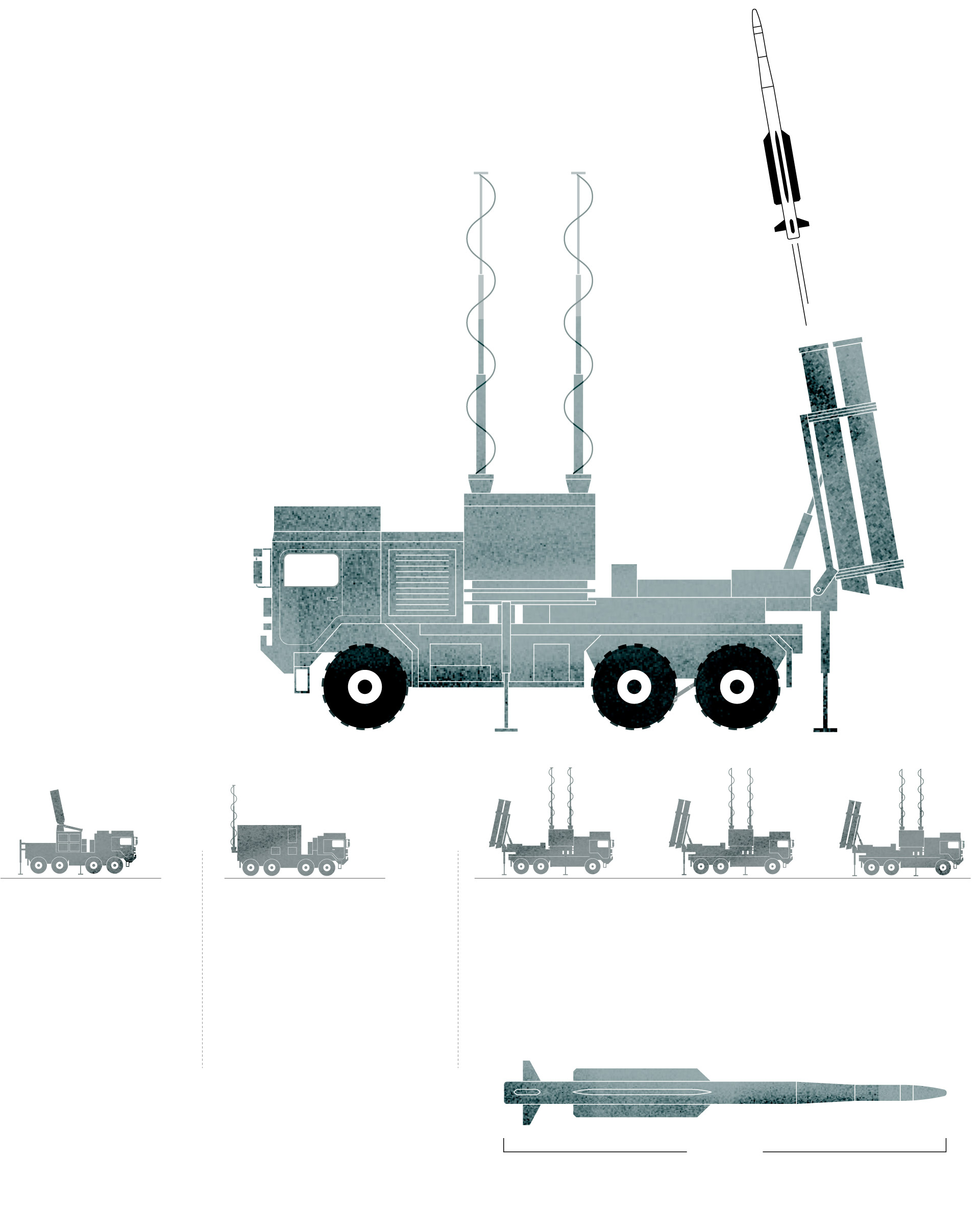
IRIS-T SL system
components
The IRIS-T SL is a mobile air defense missile system designed and developed by the German company Diehl.
Launcher
The launcher vehicle can be based on a truck chassis or a tracked armored chassis. In the firing position, the container missile launchers are erected in the vertical position.
Radar
The system includes a multifunction radar with a range of 250 km (155 miles).
Command and
Control System
It performs fire control used to conduct airspace surveillance and has the capability to evaluate aerial treats and weapon assignments.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
The Hawk system is the predecessor to the Patriot. Some versions are up to 50 years old.
It is no longer used in the United States, but many U.S. allies still operate the Hawk, including Spain which has sent the system to Ukraine. The United States took some Hawks out of storage to send to Ukraine as well. While the system is older than others Ukraine has, it can be useful against some lower-quality Russian missiles.
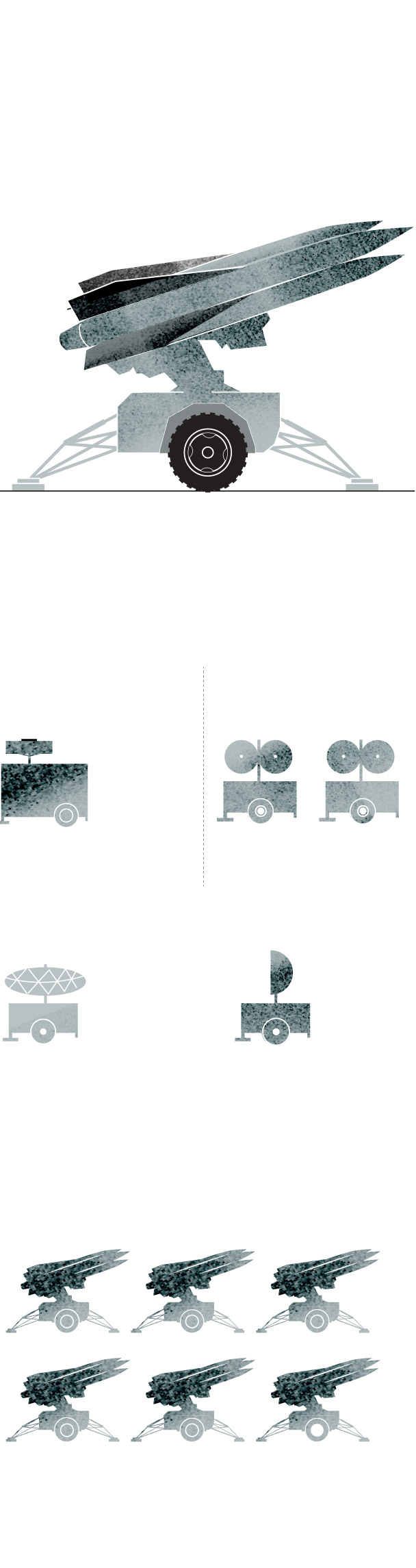
The Hawk system is the predecessor to Patriot missile defense. It provides defense against aircraft, cruise missiles and short-range tactical ballistic missiles.
The current version of the system, upgraded continuously, is called Improved Hawk or I-Hawk.
Battery Control
Central
It performs
command
and control
functions.
These track and
illuminate the targets.
A typical unit has six launchers. In addition
to their missile aiming function, they support
pre-launch commands and transport the missiles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
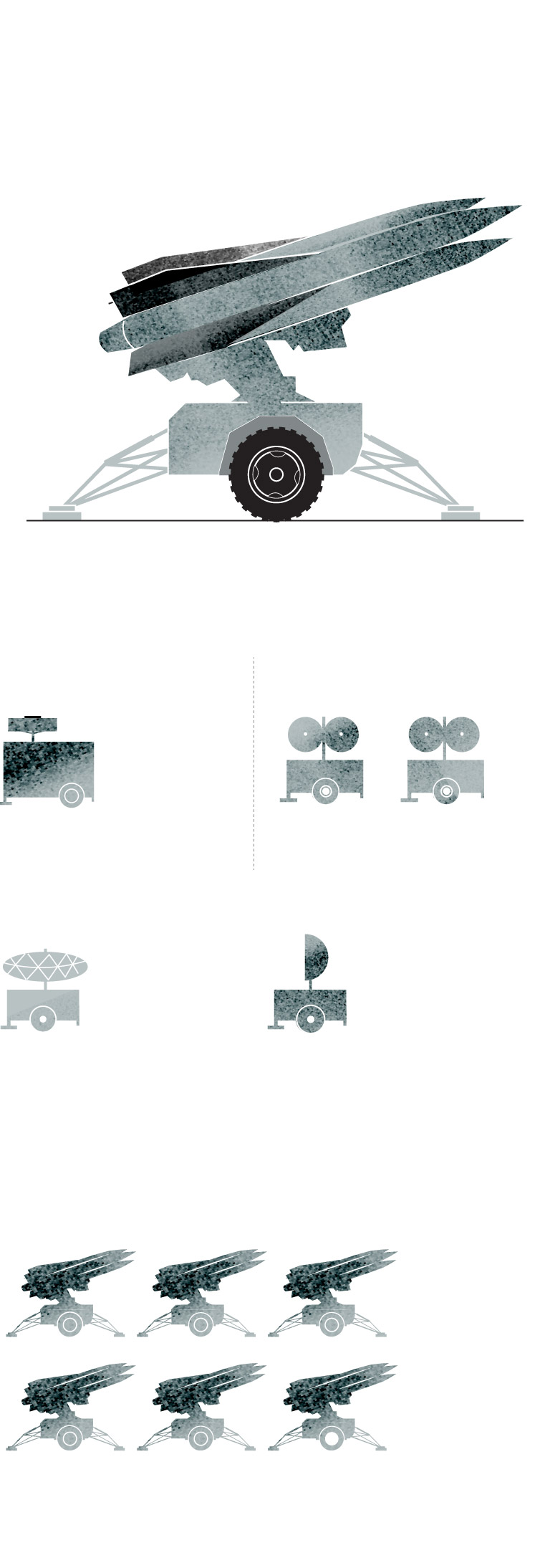
The Hawk system is the predecessor to Patriot missile defense. It provides defense against aircraft, cruise missiles and short-range tactical ballistic missiles.
The current version of the system, upgraded continuously, is called Improved Hawk or I-Hawk.
Battery Control Central
It performs
command
and control
functions.
These track and illuminate
the targets.
A typical unit has six launchers. In addition to their missile
aiming function, they support pre-launch commands
and transport the missiles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
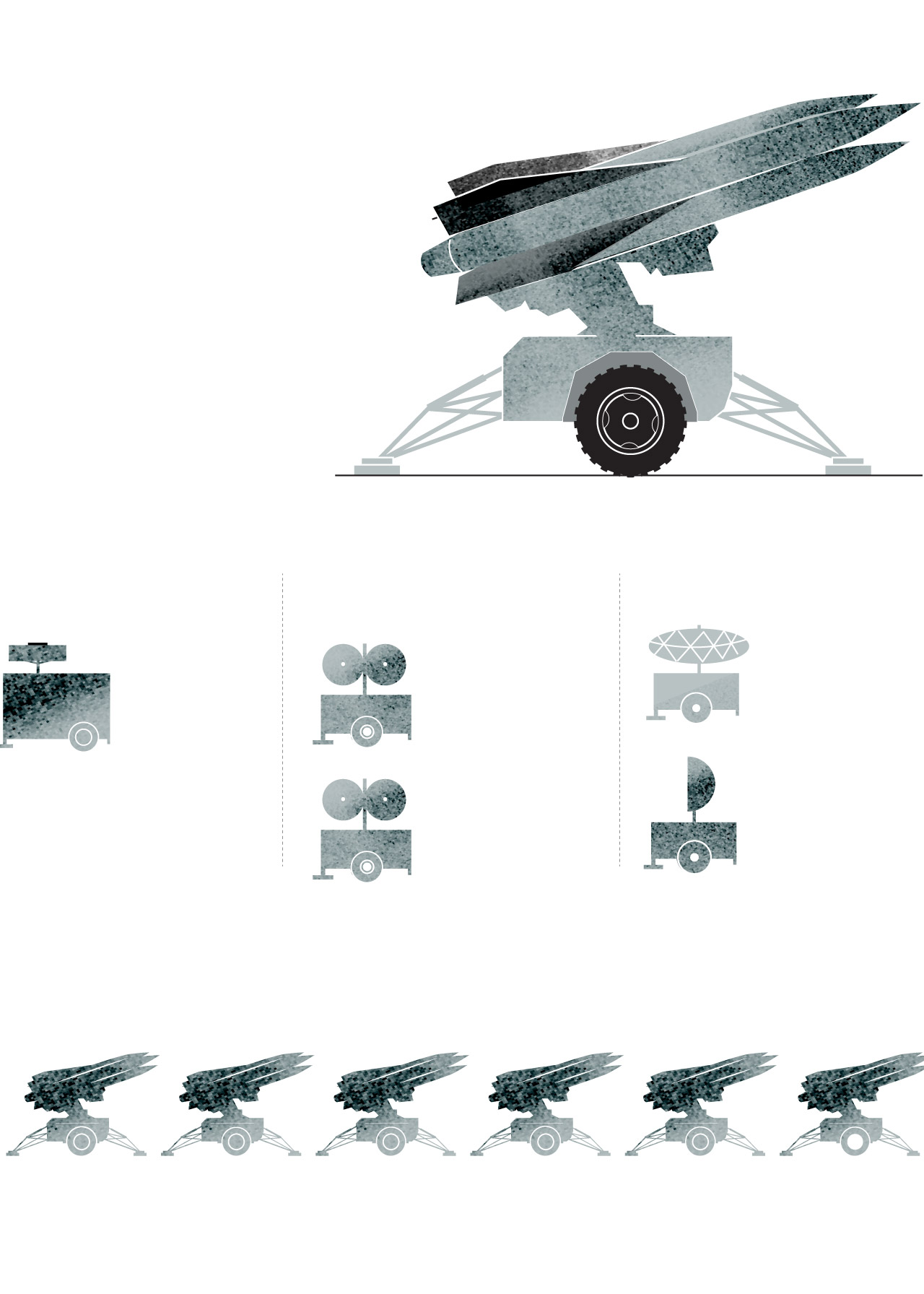
The Hawk system is the predecessor to Patriot missile defense. It provides defense against aircraft, cruise missiles and short-range tactical ballistic missiles.
The current version of the system, upgraded continuously, is called Improved Hawk or I-Hawk.
Battery Control Central
These track
and illuminate
the targets.
It performs
command
and control
functions.
A typical unit has six launchers. In addition to their missile aiming function,
they support pre-launch commands and transport the missiles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
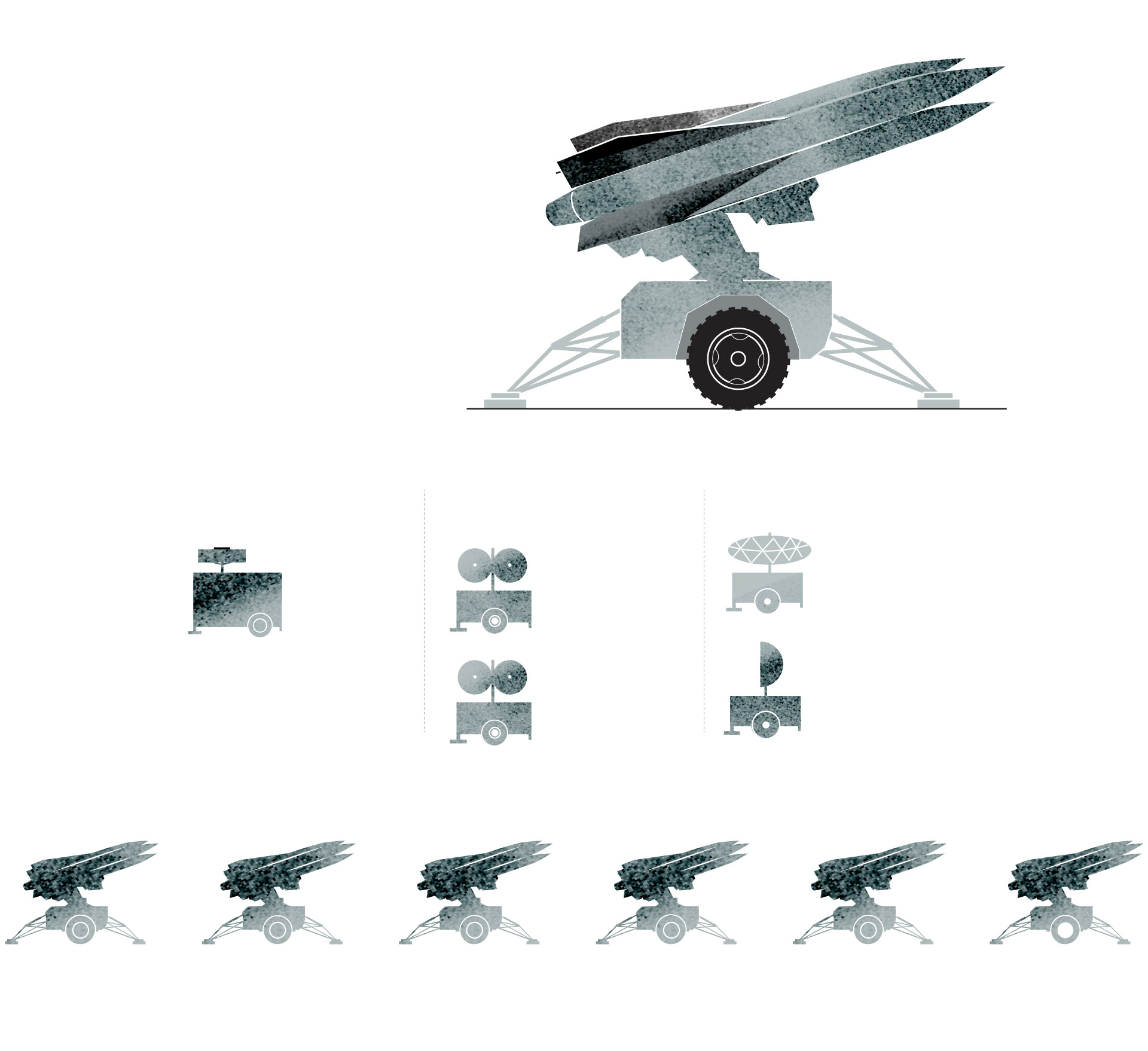
The Hawk system is the predecessor to Patriot missile defense. It provides defense against aircraft, cruise missiles and short-range tactical ballistic missiles.
The current version of the system, upgraded continuously, is called Improved Hawk or I-Hawk.
Battery Control Central
These track
and illuminate
the targets.
It performs
command
and control
functions.
A typical unit has six launchers. In addition to their missile aiming function, they support pre-launch commands and transport the missiles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
While gun trucks have a much shorter range than other air defense systems, their ammunition is more readily available and cheaper. It’s a more basic system which can easily be operated by soldiers who only need to see a threat and fire.
They have been most useful, Williams said, in intercepting Iranian-made drones that Russia has used. “Gun systems have been really good at helping Ukrainians preserve their interceptor capacity,” he said. That has helped commanders save more complex and expensive systems for bigger threats, like aircraft and missiles.
The Pentagon said last month it would provide nine such trucks armed with 30mm cannons, along with laser-guided rockets. Both systems, officials said, are intended to be used against drones.
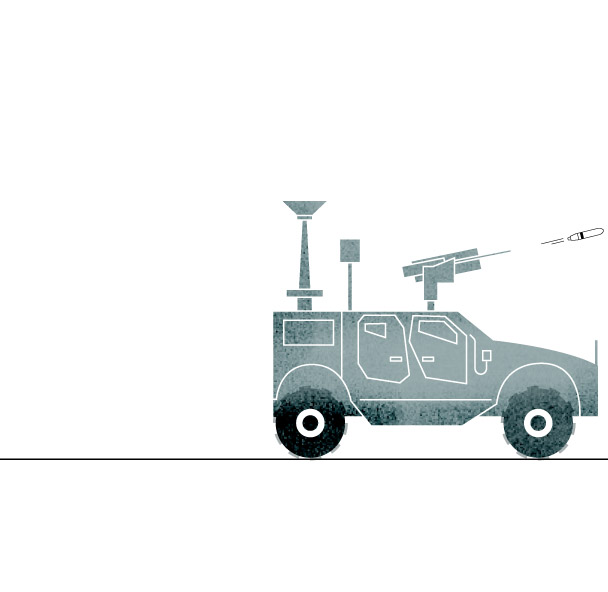
Counter-Unmanned
Aerial System
The 30mm gun trucks can detect, track and shoot air targets like drones, but also can fire on ground-based threats like enemy vehicles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
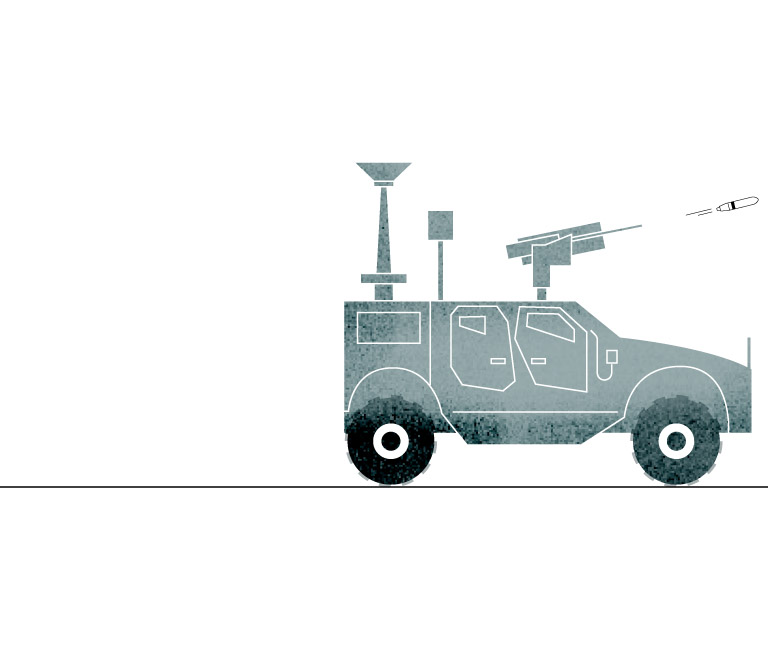
Counter-Unmanned
Aerial System
The 30mm gun trucks can detect, track and shoot air targets like drones, but also can fire on ground-based threats like enemy vehicles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
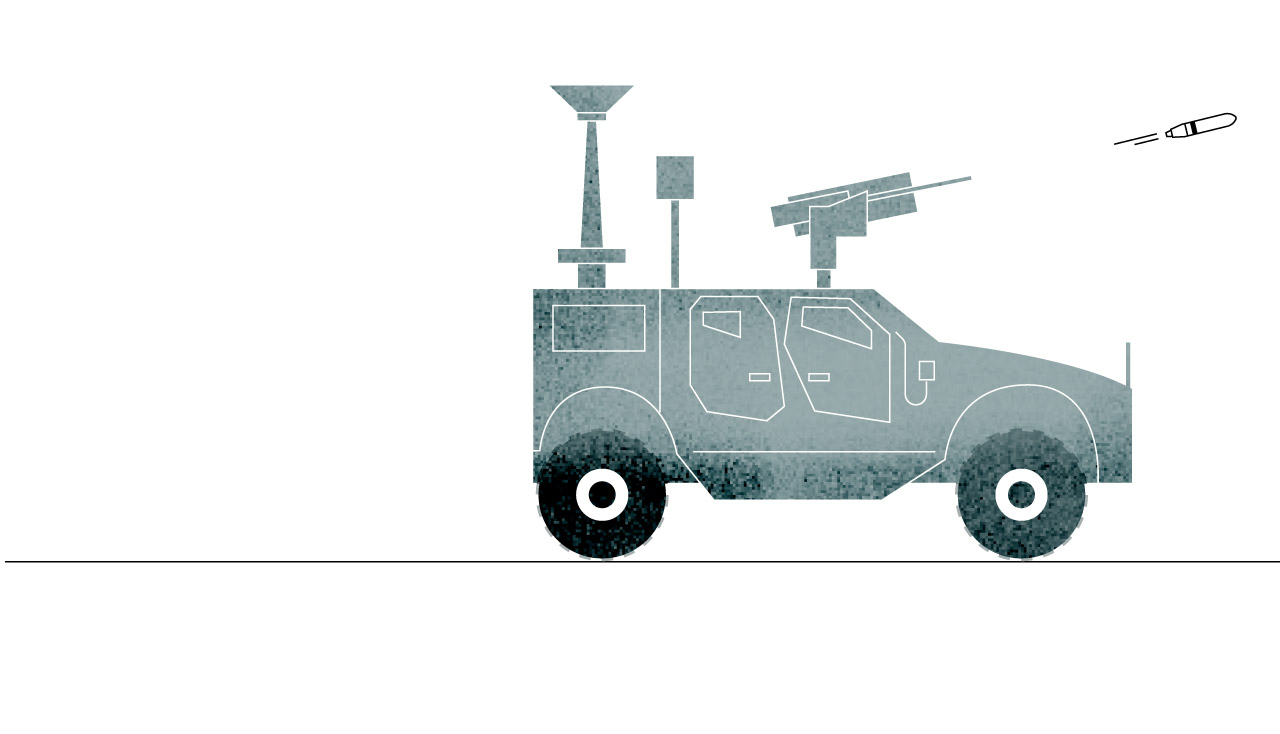

Counter-Unmanned
Aerial System
The 30mm gun trucks can detect, track and shoot air targets like drones, but also can fire on ground-based threats like enemy vehicles.
Sources: Army Recognition Group.
Karen DeYoung and Serhiy Morgunov contributed to this report.
[ad_2]
Source link

